Cannabinoids are compounds found in two places in nature: first, naturally occurring cannabinoids are found in the resin of the cannabis plant (these are called phytocannabinoids); second, cannabinoids are naturally synthesized inside the human body (these are called endocannabinoids).
“Cannabinoid” refers to any compound that has an effect on the Endocannabinoid System, which is a system of chemical messengers present in our bodies. Phytocannabinoids and endocannabinoids are similarly shaped chemicals and therefore have similar effects on the body’s Endocannabinoid System. We will discuss the Endocannabinoid System in more detail with our next blog post, but what you need to know now is that many of the effects you feel from cannabis come from the interaction between cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System. For example, Cannabinoids that engage the Endocannabinoid System in the “reward center” of the brain can cause a release of the neurotransmitter Dopamine, which results in a feeling of euphoria. Cannabinoids engaging the Endocannabinoid System along pain centers can result in blocking the pain signal which results in pain relief.
The earliest research into cannabinoids leads back to 1940 and the identification of CBN. Two years later CBD was first isolated. Later on in 1964, Dr. Raphael Mechoulam from the Israeli Weismann Institute of Science succeeded in isolating Delta 9-THC which would revolutionize the way Cannabis was perceived. However, it wasn’t until the early 1990s that the human receptors for cannabinioids (namely, CB1 and CB2) were isolated. These findings have accelerated cannabis research: a recent assessment of cannabis research showed that while the overall annual number of scientific publications increased 2.5 times between 2000–2017 the corresponding number for publications on cannabis increased 4.5 times and increased 9-fold for publications on medical cannabis.
There are over 100 different known cannabinoids, but we’ll highlight the cannabinoids you are most likely to find in Maryland Cannabis Flower and Concentrates.
Top 6 Cannabinoids Found in Cannabis:
- Delta 9-THCA: Naturally occurring, non-psychoactive precursor to THC
- Delta 9-THC: The more biologically active form of THC that has medicinal and
psychoactive properties - CBD: Non-psychoactive. Best known for its ani-inflammatory and anti- anxiety properties
- CBG: Non-psychoactive. Best known for it’s ability to treat pain and depressed mood
- THCV: Mildly psychoactive. Best known for appetite manipulation
- CBN: Mildly psychoactive and most known for it’s sedative properties
Cannabinoids Soon to Be More Available in Cannabis Products:
- Delta 8-THC: Known for psychoactive and anti-nausea effects
- CBC: Non-psychoactive and most known for pain treatment
Let’s discuss each cannabinoid in more detail:
THCa is a non-psychoactive acidic precursor to THC and is naturally found in the resin of the cannabis plant. When the resin is heated , the acid part of the molecule drops off and THCa then converts to THC. This process is known as decarboxylation. An analogy that might help describe this process is making bread: think of THCa as the dough before it is baked in the oven. You then apply heat to the dough and it and becomes edible bread (THC).
You will notice that most products’ test results show high levels of THCa and low levels of THC. This is because the products have not yet been exposed to heat and the THCa has not yet been converted to THC. Then when you bring the product home and expose it to high levels of heat, like a flame from a lighter or an oven, it is converted from THCa to THC.
Most of the THCa will be converted to THC, but small amounts of THCa will still be present. Once the acid group drops off, the THC is able to tightly bind the receptors in the Endocannabinoid System. THCa (with the acid group) can still engage the Endocannabinoid System but it is much weaker than THC without the acid group.
Conditions THCa Has the Potential to Help With:
- Inflammation
- Nausea
- Appetite Loss
- Epilepsy
- Pain
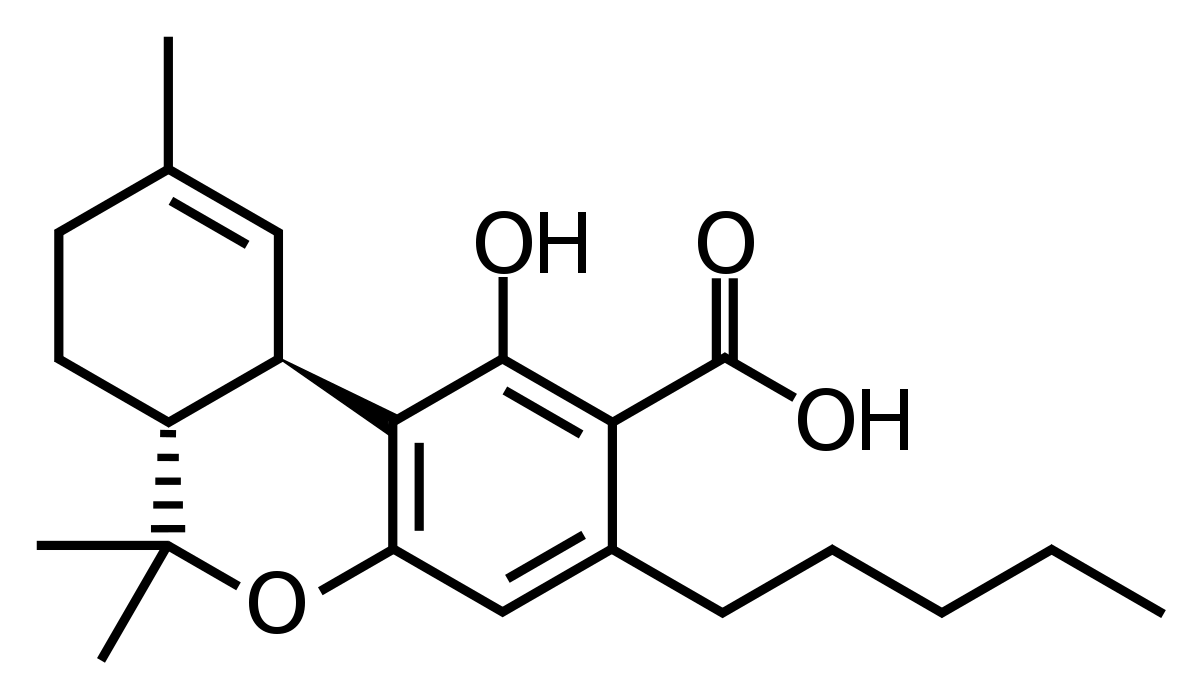
This is the biologically active form of THC you’re most familiar with when referring to cannabis. THC was first isolated in 1964 By Dr. Raphael Mechoulam at the Israeli Weismann Institute of Science. Delta 9-THC binds tightly to the naturally occurring cannabinoid receptors in the body that are part of the Endocannabinoid System. The binding of delta 9-THC to these receptors results in changes in chemical signaling between the cells of the body. The effects of this binding include decreased pain, decreased nausea and sleepiness. Delta 9-THC is listed as ‘THC’ on each product label.
Short Term Effects of Delta 9-THC:
- Pain Relief
- Decreased nausea
- Sleepiness
- Decreased anxiety and stress
- Increased appetite
- Relaxation
- Euphoria
Conditions Delta 9-THC Has the Potential to Help With:
- Pain: chronic, neuropathic, migraine, arthritic
- Inflammation
- PTSD
- Insomnia
- Nausea
- Cancer and Chemotherapy Symptoms
- Crohn’s Disease (inflammatory)
- Fibromyalgia
- Alzheimers
- Multiple Sclerosis (spasticity)
- Glaucoma
- ADHD
- Appetite Loss
These are just some of the conditions for which THC has shown to potentially provide relief. More research is needed.
Strains in Maryland High in THC:
- Motor Breath #15
- Garlic Cookies
- Dosidos #22-22
- Kush Mints
- Birthday Cake
- Tahoe Alien
- Black Afghan
- Yuck Mouth
- Cinderella 99
- Poochie Love
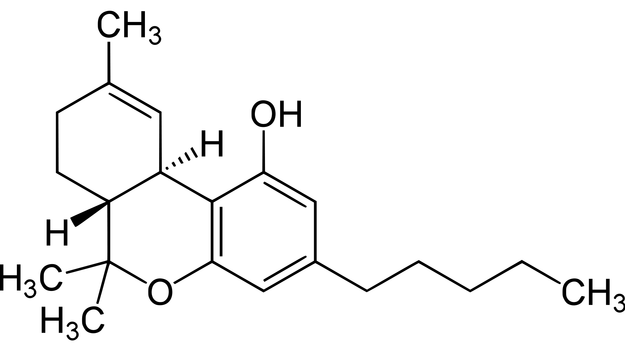
After THC, CBD is the next most widely known compound in the Cannabis plant. CBD is non-psychoactive and has gained a lot of attention for its potential to help with epilepsy. CBD does not bind to the receptors that make up the Endocannabinoid System. Rather, it affects other substances that do modulate the Endocannabinoid System. CBD is known to interact with other cannabinoids, namely THC. It is known that CBD taken before THC can augment the effects of THC. Conversely, CBD taken after THC can reduce the effects of THC – which is very helpful when a patient has unwanted side effects from taking too high of a dose of THC.
Conditions CBD Has the Potential to Help With:
- Anxiety
- Pain/Inflammation
- Insomnia
- PTSD
- Epilepsy/Seizures
- Impulse Control/Drug Addiction/Smoking Cessation
- Opioid Withdrawal/Opioid Cravings
Strains in Maryland High in CBD:
- Harlequin
- Mango CBD
- Cannatonic
- AC/DC
- Shark Shock
- White Harmony
- Euphoria
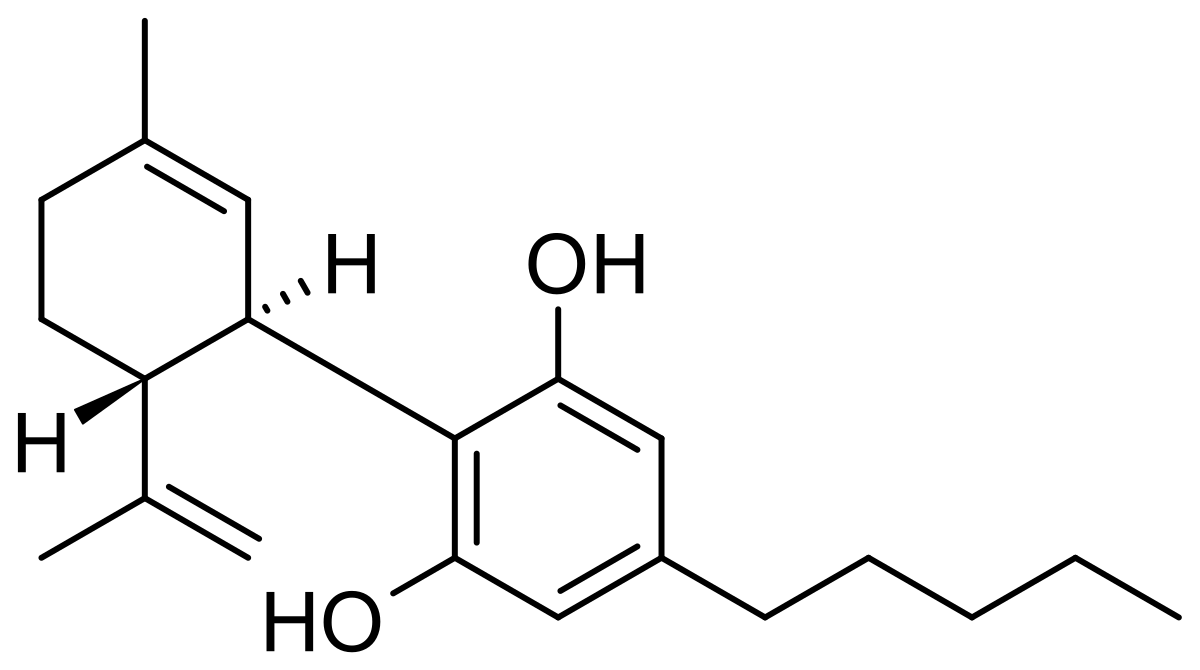
CBG is a non-psychoactive Cannabinoid typically most abundant in low THC and high CBD strains. CBG is the precursor to the better known cannabinoids THC and CBD:
Theoretically, a grower could harvest a crop with a high percentage of CBG if they just harvested the plants early, before they were able to convert CBG into THC or CBD. CBG is a weak binder of the receptors of the Endocannabinoid System.
Conditions CBG Has the Potential to Help With:
• Glaucoma
• IBD (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
• Cancer and Chemotherapy Symptoms
• Infection
• Appetite Loss
• Pain
• Depression
There aren’t currently any CBG dominant products on the market, though some low THC and high CBD stains can contain considerable amounts of CBG.
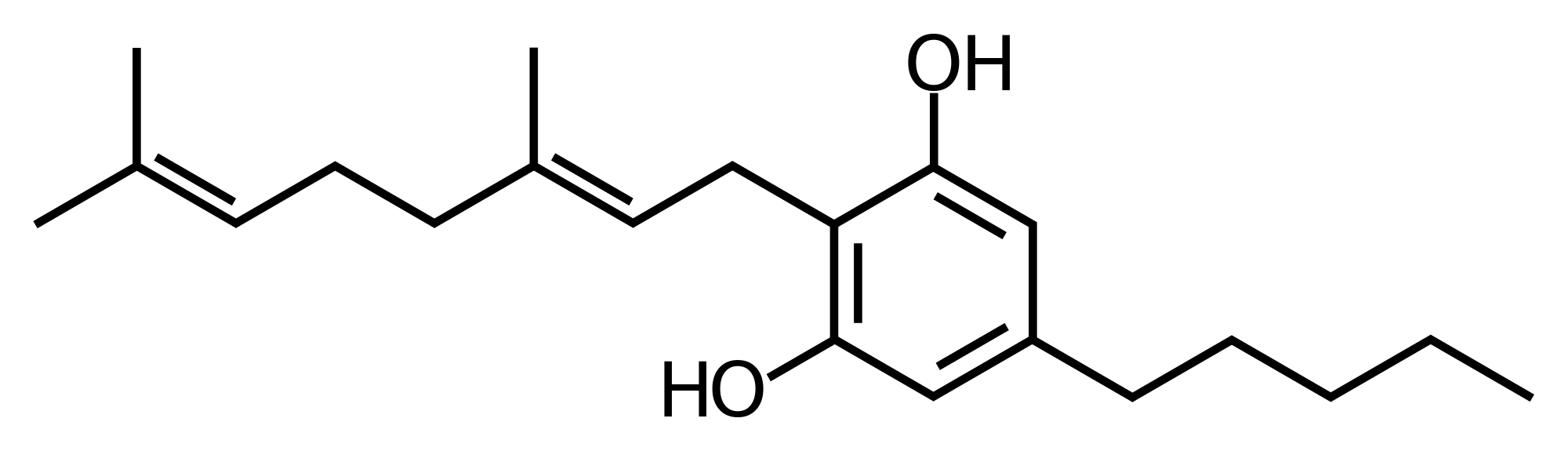
THCV is similar in molecular structure to THC. THCV is mildly psychoactive and is most often found in African Landrace Cultivars. Like many cannabinoids, the effects of THCV are biphasic, which means that in lower concentrations it can act as an appetite suppressant and in larger concentrations it can potentially stimulate appetite.
Conditions THCV Has the Potential to Help With:
- Hunger
- May help regulate blood sugar
- Anxiety
- Building bone in patients with low bone density conditions
Strains in Maryland High in THCV:
- Texas Shoreline
- Guice
- Durban Poison
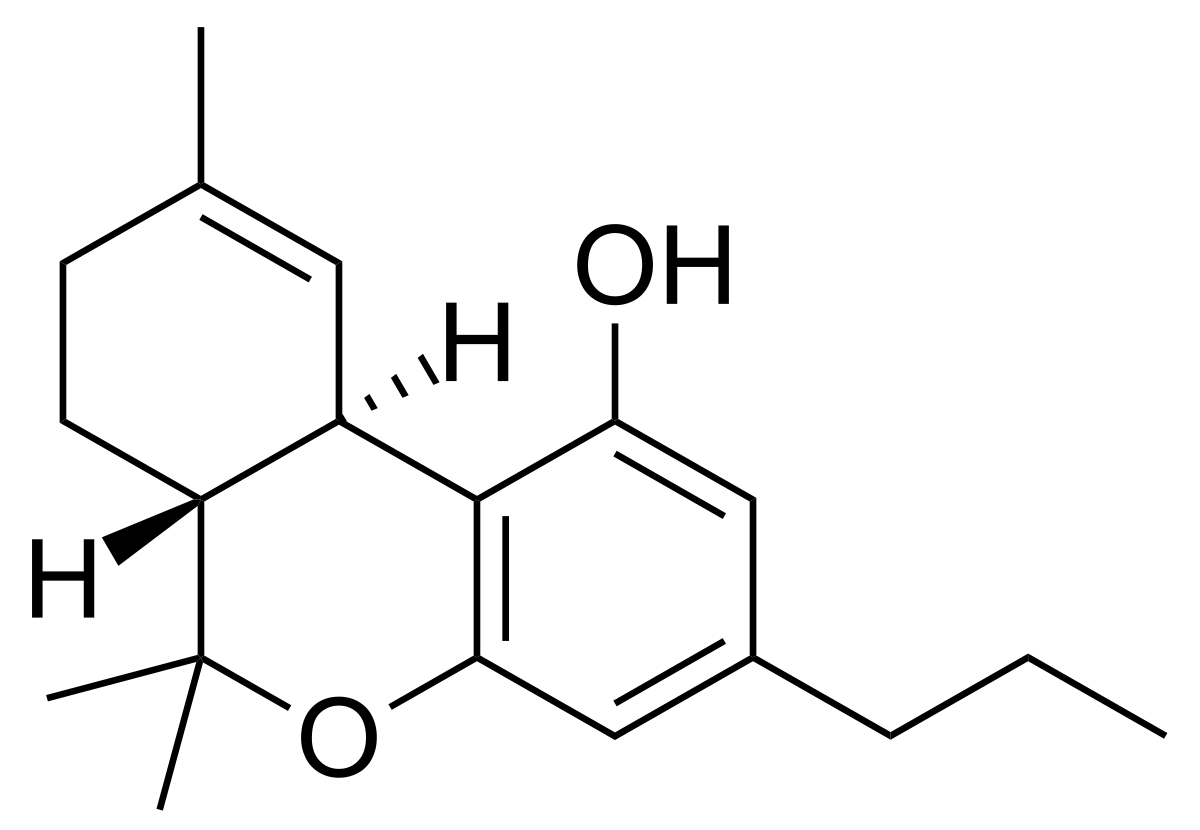
CBN is mildly psychoactive and is a natural degradation product of THC. The presence of CBN in a strain typically means that the strain will have more sedative qualities. CBN is a partial agonist of CB1 receptor of the Endocannabinoid System and has a strong affinity for the CB2 receptor of the Endocannabinoid System.
Conditions CBN Has the Potential to Help With:
- Inflammation
- Appetite Loss
- Glaucoma
- Insomnia
- Infection
- Neuroprotectant
Products in Maryland High in CBN:
- Feel Dreamy Feel Collection 1:1 THC:CBN Tincture
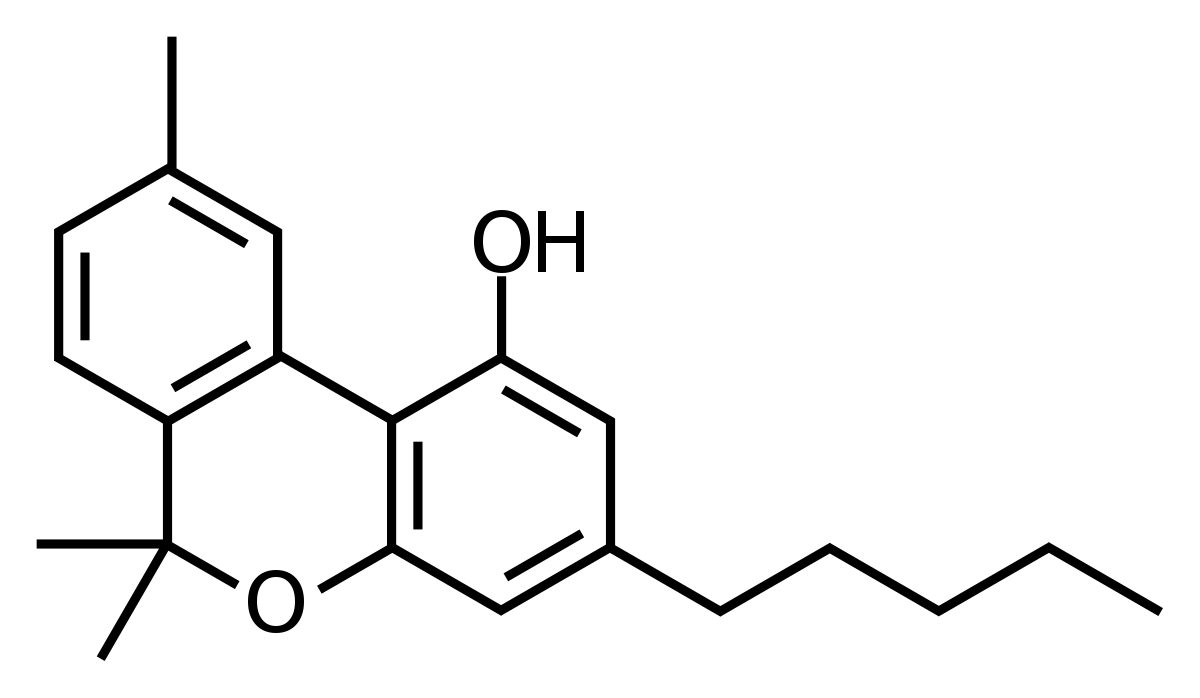
Delta 8-THC is a minor Cannabinoid found in the resin of the cannabis plant. It also can be synthesized in the lab using either delta-9 THC or CBD. Like delta 9-THC, delta 8-THC binds to the CB1 receptors in the central nervous system. Typically, delta 8-THC is found in extracted products because it naturally exists in very small levels within the Cannabis resin. Advances in cultivation practices may allow us to see cultivars with higher levels of these minor cannabinoids someday.
Conditions Delta 8-THC Has the Potential to Help With:
- Anxiety
- Nausea
- Appetite Loss
Delta 8-THC is not widely available in the Maryland Cannabis Market. While Delta 8-THC has always been on the Controlled Substances List, there had been hope of a hemp loophole with the 2018 Farm Bill: that delta 8-THC derived from hemp was legal as long as the delta 9-THC portion was below 0.3%. This is still a legal grey area, but the good news is that anyone purchasing products with delta 8-THC from a licensed dispensary is still on firm legal ground since our regulatory body does not oversee the production of hemp.
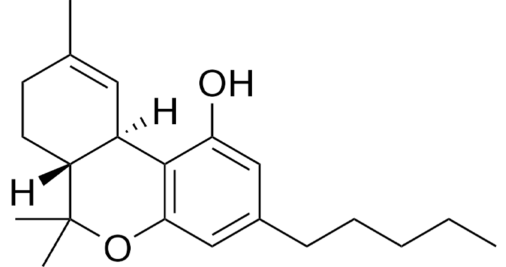
CBC is one of the primary cannabinoid lines derived from the parent molecule CBG (along with THC and CBD). CBC is non-psychoactive and engages cannabinoid receptors involved in the regulation of sensitivity to pain. Importantly, CBC is thought to enable other substances present in the resin of the plant to work better together – this is commonly referred to as the Entourage Effect.
Conditions CBC Has the Potential to Help With:
- Cancer and Chemotherapy Symptoms
- Pain
- Inflammation
- Acne
- Depression
There aren’t currently any CBC dominant products on the market. It’s suggested you research cannabinoid profiles of products when seeking CBC because CBC can potentially be found in Cartridges and Concentrates.
Cannabinoids have a range of psychoactivity and a variety of potential medicinal uses, from pain relief to appetite stimulation. With the discovery of the key compounds in the plant’s resin as well as a better description of the body’s naturally occurring Endocannabinoid System, research in this area of plant-based medicine is really taking off. We are also finally able to begin researching some of the lesser-known cannabinoids to better understand how they behave, both in isolation and together.
Most cannabinoids are thought to be considered biphasic, meaning in smaller amounts they may be useful in treating your conditions, and in larger amounts, the results may be less desirable. For example, THC in smaller doses may help someone suffering from anxiety, while a larger dose may actually exacerbate the discomfort. This is why we advocate for the “slow and low” method of medicating. While we’re beginning to have a broader understanding of how these compounds act independently, much more research is needed to fully understand how they work together.
We suggest patients pay close attention to the Cannabinoid profiles found on the label of every product purchased from a Maryland dispensary. One technique patients may find useful is to journal or take notes when they medicate so they can compare different strains and their effects. This is especially important because each person can have a different experience because our body chemistries are naturally different.
If you have additional questions regarding cannabinoids, don’t hesitate to ask your patient care associate during your next visit to Ritual Dispensary. We’re always happy to help!
Disclaimer: Much of the information in this article is experience-based and not yet proven by clinical research. Further research is required. Please consult with your medical physician before starting a medical cannabis program.